Early Childhood Care and Education: Why It Matters?
Early Childhood Care and Education:
Why It Matters?
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) is a term that
encompasses the physical, cognitive, social, and emotional development of
children from birth to eight years of age. ECCE is crucial for the holistic
development of children, as it lays the foundation for their lifelong learning,
well-being, and success.
In this blog post, we will explore some of the key benefits
of ECCE for children and society, as well as some of the challenges and
opportunities for improving its access and quality.
Need and Importance
of ECCE
Early childhood care and education
(ECCE) is a crucial stage in the development of children. It refers to the
provision of quality care, learning, and stimulation for children from birth to
eight years of age. ECCE has multiple benefits for children, families, and
society. It can enhance children's cognitive, social, emotional, and physical
skills, prepare them for formal schooling, and foster lifelong learning. It can
also support parents and carers in their roles and responsibilities and promote
gender equality and social inclusion. ECCE is a human right and a public good
that contributes to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals.
ECCE also has
long-term benefits for the child and society. Children who receive quality ECCE
are more likely to enrol in school, perform better academically, complete
higher levels of education, earn higher incomes, and contribute positively to
the social and economic development of their communities. They are also less
likely to drop out of school, engage in risky behaviours, suffer from mental
health problems, or become involved in crime or violence.
Key aspects of Early
Childhood Education
1. Developing curiosity: Children are naturally curious and eager to explore the world around them. By providing them with stimulating and engaging activities, teachers can foster their curiosity and encourage them to ask questions, make observations, and experiment with different materials and ideas.
2.
Logical thinking and problem-solving: Children
can develop their logical thinking and problem-solving skills by participating
in activities that challenge them to use their reasoning, creativity, and
imagination. For example, they can solve puzzles, play games, build structures,
create stories, and invent solutions to real-life problems.
3.
Teamwork and collaboration: Children
can learn to work together and cooperate with others by engaging in group
projects, discussions, role plays, and cooperative games. They can also learn
to respect diversity, appreciate different perspectives, and communicate
effectively with their peers and teachers.
4. Arts, crafts, and music: Children can express themselves creatively and artistically by exploring various forms of arts, crafts, and music. They can also develop their fine motor skills, sensory awareness, aesthetic appreciation, and cultural understanding by using different materials, tools, instruments, and techniques.
5. Relationship
with nature: Children can develop a sense of
connection and appreciation for nature by spending time outdoors, observing and
interacting with plants, animals, and natural phenomena. They can also learn
about environmental issues, sustainability, and conservation by engaging in
eco-friendly practises and projects.
6. Colours,
shapes, alphabets, and numbers: Children can acquire basic
literacy and numeracy skills by learning about colours, shapes, alphabets, and
numbers. They can also develop their vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and
comprehension by listening to stories, songs, rhymes, and poems.
7.
Play-based and discovery-based learning: Children
can learn through play and discovery by choosing their own activities,
interests, and goals. They can also learn from their own experiences, mistakes,
and successes by reflecting on their actions and outcomes.
8.
Ethics: Children
can learn about ethics by developing a sense of right and wrong, fairness and
justice, empathy, and compassion. They can also learn to respect themselves and
others, follow rules and norms, take responsibility for their actions and
consequences, and resolve conflicts peacefully.
9.
Self-identity: Children
can learn about self-identity by developing a sense of who they are, what they
like and dislike, what they are good at, and what they need to improve. They
can also learn to appreciate their strengths, talents, abilities, and potential.
10.
Etiquette, behaviour, and emotional
development: Children can learn about
etiquette, behaviour, and emotional development by developing a sense of
self-regulation, self-control, self-esteem, and self-confidence. They can also
learn to manage their emotions, cope with stress, express their feelings and
needs appropriately, and respond to others' emotions sensitively.
Benefits of ECCE for Children
ECCE has a positive impact on children's well-being and development in various domains. Some of the benefits of ECCE for children are:
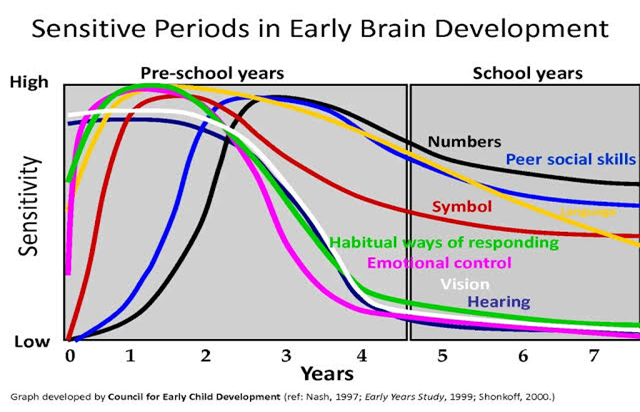
ECCE stimulates brain development and enhances cognitive skills such as memory, attention, language, and problem-solving. Research shows that the brain develops most rapidly in the first five years of life and that early stimulation and interaction can have lasting effects on brain structure and function.The above picture illustrates the preschool years, from birth to five years old. This is a critical time for child brain development, as it offers many opportunities for children to develop holistically.
1.
ECCE fosters social and emotional skills such
as self-regulation, empathy, cooperation, and resilience. These skills are
crucial for children's ability to form healthy relationships, cope with stress
and challenges, and adapt to different situations and environments.
2. ECCE
supports physical and motor development, such as coordination, balance,
strength, and health. ECCE provides opportunities for children to engage in
physical activities, play, and exploration that promote their physical
well-being and prevent obesity and chronic diseases.
3. ECCE
nurtures moral and ethical development, such as values, attitudes, beliefs, and
behaviours. ECCE exposes children to diverse cultures, perspectives, and experiences,
which help them develop a sense of identity, respect, tolerance, and
responsibility.
Benefits of ECCE for Society
ECCE benefits not only children individually but also society
collectively. Some of the benefits of ECCE for society are:
1.
ECCE reduces poverty and inequality as it
improves children's educational outcomes and future earnings. ECCE prepares
children for school readiness and success, which increases their chances of
completing primary and secondary education, pursuing higher education, and
entering the labour market. ECCE also reduces the intergenerational
transmission of poverty as it enables parents to work or study while their
children are in safe and stimulating environments.
2.
ECCE improves health and nutrition outcomes as
it prevents or mitigates the effects of malnutrition, disease, and injury. ECCE
provides children with adequate food, water, sanitation, hygiene, and health
care services that protect them from hunger, dehydration, infection, and
trauma. ECCE also educates children about healthy habits and practises, such as
washing hands, brushing teeth, and eating fruits and vegetables.
3. ECCE
enhances gender equality and empowerment as it promotes girls' education and
participation. ECCE ensures that girls have equal access to quality learning
opportunities and resources, which boost their confidence, self-esteem, and
aspirations. ECCE also challenges gender stereotypes and norms, such as those
related to roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
4. ECCE
promotes social cohesion and peacebuilding as it fosters social capital and
civic engagement. ECCE creates a sense of community and belonging among
children, families, and educators, which strengthens their trust, cooperation,
and solidarity. ECCE also cultivates a culture of peace and non-violence among
children, who learn to respect diversity, resolve conflicts peacefully, and
advocate for their rights.
Challenges and
Opportunities for Improving ECCE
Despite the proven
benefits of ECCE, many children around the world still lack access to quality
ECCE services. According to UNESCO (2020), only 48% of children under five
years old participate in some form of organised early childhood education
programme globally.
ECCE faces many challenges in different contexts, such as a lack
of resources, trained teachers, supportive policies, parental involvement,
cultural diversity, and equity. These challenges hinder the access, quality,
and outcomes of ECCE programmes and services, especially for the most
vulnerable and marginalised children.
To overcome these challenges, ECCE needs to adopt a holistic and integrated approach that addresses the multiple dimensions of early childhood development, such as health, nutrition, protection, stimulation, and learning. ECCE also needs to engage with various stakeholders, such as governments, civil society, the private sector, donors, and communities, to ensure coordination, collaboration, and accountability. ECCE also needs to leverage the potential of technology and innovation to enhance the delivery and effectiveness of its interventions.
By addressing these challenges and seizing these opportunities, ECCE can contribute to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 4 on quality education for all. ECCE can also promote social cohesion, economic growth, and human rights for current and future generations.




Comments
Post a Comment